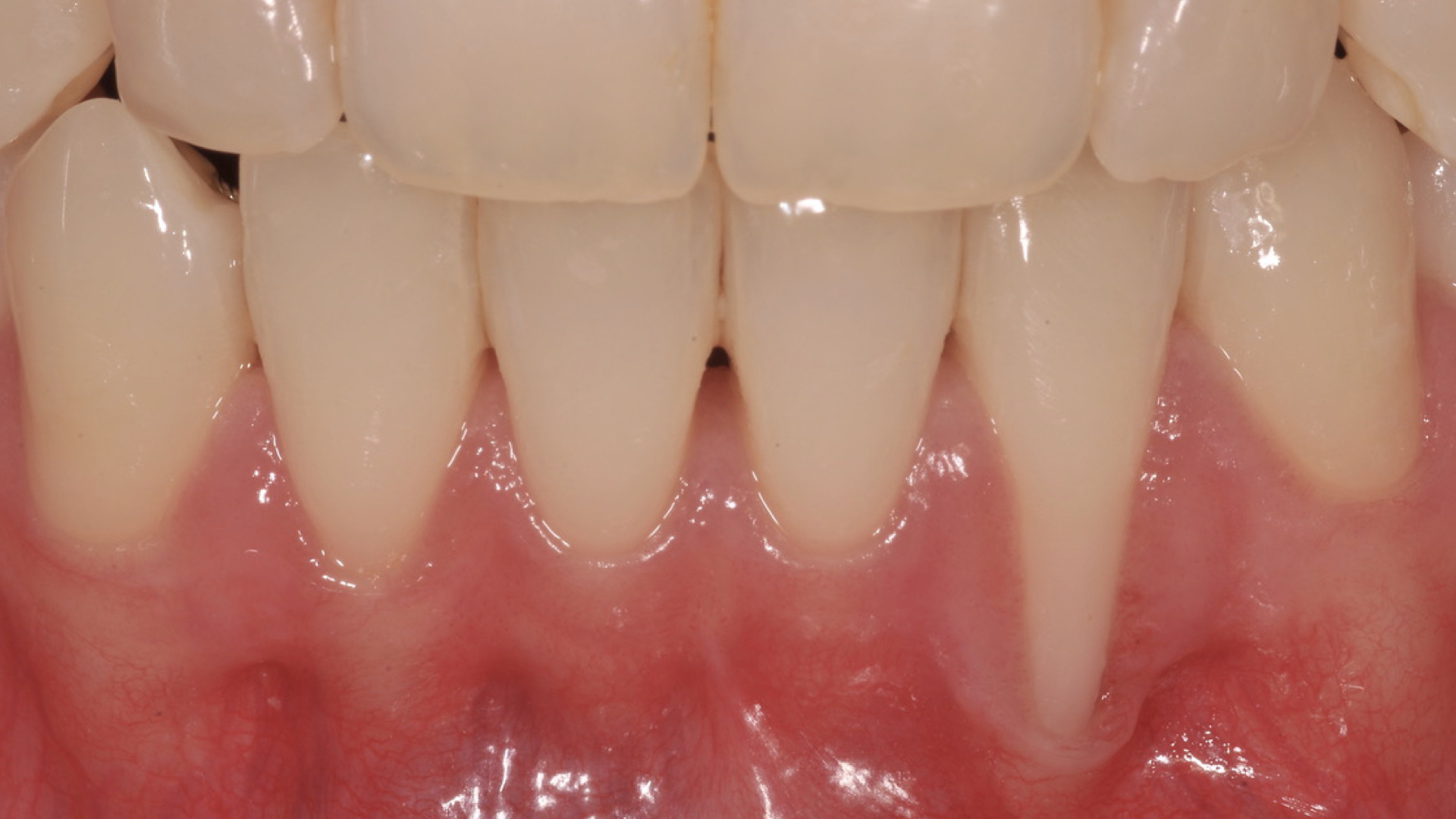
Your teeth’s health depends on your gums’ health
buy Gabapentin online from usa Periodontology is the branch of dentistry that http://thelittersitter.com/1index.php prevents and treats problems of the periodontium, which are the tissues that support and maintain the teeth (gingiva, alveolar bone, cementum, periodontal ligament) through deep cleanings, which eliminate plaque and calculus, curing gingivitis and periodontitis.
Regular check up visits enables your doctor to diagnose early periodontal disease and to quickly take preventative and therapeutic measures.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is an inflammation which causes sensibility and bleeding of the gingival tissues following a buildup of dental plaque. It is curable by simply removing this plaque during one or several professional cleanings and maintaining good home oral hygiene.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis or periodontal disease is a bacterial infection that in addition to other aiding factors (smoking, hereditary predisposition, etc.) damages the periodontium, supporting gingival and osseous tissues and other tissues surrounding the teeth. Often periodontitis does not present with painful symptoms, therefore, it may be that a patient does not realize that he or she is suffering from this disease until the clinical symptoms become more evident. These symptoms may include bleeding gum tissues, halitosis, mobility and eventually tooth loss.
The treatment of periodontal disease is dependent on its severity. In the initial stages of the disease it may be simply treated through the removal of plaque, calculus and inflamed tissues from the sub gingival surfaces of the teeth in the periodontal pocket of the area affected. This deep cleaning procedure which includes cleaning underneath the gingival tissues (called scaling and root planing or root debridement) removes plaque and calculus from the periodontal pockets favoring reattachment of the gingival tissues to the newly cleaned, smooth and decontaminated root surfaces of the tooth. This reattachment of the soft tissues to the root surface is then thus an inhibitor to new plaque accumulation. When periodontal disease is more severe it may be necessary to intervene surgically in office, in order to reconstruct the deeper periodontal tissues (bone and ligament) and the more superficial tissues (gingiva).